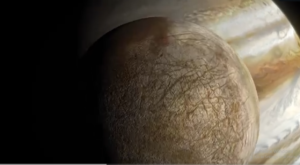
NASA has launched mission to investigate a the habitable ocean world for the mankind
The largest spacecraft ever built of the exploration on the outer space Europa clipper , launched from NASA Kennedy space center to determine that the Jupiter Europa moon could be habitable or not . the clipper would be the NASA’s first spacecraft for the exploration of the Jupiter moon Europa Jupiter’s moon Europa — launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket Monday at 12:06 p.m. ET from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

Europa Clipper is a NASA mission designed to explore Europa, one of Jupiter’s largest moons, and one of the most intriguing places in our solar system for the potential of finding life. The mission aims to investigate Europa’s icy shell and the subsurface ocean believed to exist beneath it. Here’s a breakdown of what the Europa Clipper mission is and its objectives:
Key Goals and Objectives:
- Study Europa’s Ice Shell:
- The spacecraft will examine Europa’s icy surface and its interactions with Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field. Europa’s ice is thought to be broken into huge plates, which could provide insights into the moon’s internal structure and whether there is heat being generated beneath the ice.
- Investigate the Subsurface Ocean:
- Europa is believed to have a vast ocean beneath its icy shell, which could potentially harbor life. The Europa Clipper will look for signs of an active ocean, including studying the interaction between the ocean and the moon’s rocky mantle. The spacecraft will also search for potential water plumes that might be venting from the surface, which could offer an easier way to sample the ocean without drilling.
- Assess Habitability:
- One of the primary reasons for sending a mission to Europa is to explore its potential for habitability. Europa Clipper will measure the chemistry of the surface and look for materials necessary for life. Understanding whether the ocean is in contact with the moon’s rocky interior is key to determining if the environment could support life.
- Study Europa’s Geology and Tidal Heating:
- Europa experiences tidal forces due to its interaction with Jupiter’s gravity, causing its ice shell to flex. This process generates heat and could be crucial for keeping the subsurface ocean warm. The mission will investigate the geological features of the surface, like the ridges, cracks, and other signs of tectonic activity.
- Examine the Moon’s Magnetic Field:
- Europa has an induced magnetic field created by interactions with Jupiter’s powerful magnetosphere. The Europa Clipper will measure this magnetic field to better understand the depth and salinity of the subsurface ocean, which could affect the moon’s electromagnetic properties.
The Spacecraft and Instruments:
- Europa Clipper is designed to orbit Jupiter and conduct flybys of Europa. Unlike other spacecraft that are designed to land, Europa Clipper will make detailed flybys, passing close to the moon up to 50 times.
- Instruments: The spacecraft is equipped with a suite of 10 scientific instruments, including cameras, spectrometers, and radar systems to map the moon’s surface, measure its composition, and investigate its subsurface ocean. These include:
- A laser altimeter for measuring the moon’s surface topography.
- A radar system to penetrate the ice and study the ocean below.
- Imaging systems to capture high-resolution photos of the surface features and look for plumes.
- Spectrometers to analyze the chemical composition of the surface and any potential plumes.
Timeline and Launch:
- Launch: Europa Clipper is scheduled to launch in 2024 aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket or another suitable launch vehicle.
- Arrival: It is expected to arrive at Jupiter in 2030 and conduct a series of close flybys of Europa, making detailed observations over a number of years.
Why Europa?
Europa is one of the most intriguing targets in our solar system because it is thought to have an environment that could support microbial life. The discovery of a subsurface ocean makes it an ideal place to search for life beyond Earth. The icy shell and the interaction with Jupiter’s gravity make Europa an active, dynamic world, and studying it could also give insights into how other icy moons or exoplanets might support life.
The Europa Clipper mission is expected to provide crucial information to help scientists understand not only Europa but also the broader possibilities for life in our solar system and beyond.
Interesting facts about Europa

Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons, is a fascinating world that has captured the interest of scientists and astronomers alike. Here are some interesting facts about Europa:
- Potential for Life: Europa is one of the top candidates in the search for extraterrestrial life in our solar system. Beneath its icy surface, scientists believe there could be a vast, salty ocean that may harbor the right conditions for life, potentially making Europa a “habitable zone” beyond Earth.
- Icy Surface: Europa’s surface is mainly composed of water ice. The ice is cracked in places, suggesting the presence of a subsurface ocean. The fractures and ridges on the surface are some of the most striking features of this moon, and they indicate the moon is geologically active.
- Magnetic Field: Europa does not have a magnetic field of its own, but it interacts with Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field. This interaction induces electric currents within Europa’s ocean, potentially creating a subsurface electromagnetic field.
- Europa’s Ocean: The ocean beneath Europa’s icy shell could be in contact with the moon’s rocky mantle, creating the possibility of underwater volcanic activity (hydrothermal vents). This interaction could provide the necessary chemical energy for life, similar to deep-sea vents on Earth.
- Surface Temperature: The surface of Europa is extremely cold, with temperatures averaging around -260°F (-162°C). Despite this, its subsurface ocean may remain liquid due to the tidal forces exerted by Jupiter’s gravity, which causes the ice shell to flex and generate heat.
- Tidal Forces: Europa experiences immense tidal forces from Jupiter’s strong gravity, which stretches and compresses the moon as it orbits the giant planet. This tidal friction could keep the subsurface ocean warm enough to remain liquid, making it one of the most intriguing places in our solar system to study.
- Water Plumes: Observations from the Hubble Space Telescope and spacecraft like Galileo and Juno suggest that Europa might be venting water vapor into space. These plumes could be sending material from the ocean beneath the icy surface into space, which might allow scientists to sample the ocean’s composition without having to drill through the ice.
- Size and Orbit: Europa is the sixth-largest moon in the solar system and has a diameter of about 1,940 miles (3,100 kilometers). It orbits Jupiter at a distance of around 390,000 kilometers (about 240,000 miles), taking about 3.5 Earth days to complete one orbit.
- Potential Future Missions: NASA’s upcoming Europa Clipper mission, set to launch in the 2020s, aims to conduct detailed reconnaissance of Europa. It will investigate the moon’s ice shell, subsurface ocean, and the moon’s geology to assess its habitability and potential for life.
- Europa’s Atmosphere: Europa has a very thin atmosphere, primarily composed of oxygen, but it is too thin to support human life. This atmosphere is likely created by radiation from Jupiter’s magnetosphere interacting with the surface ice.
Europa remains a key focus for future space exploration, particularly in the search for signs of life beyond Earth. Its unique characteristics make it one of the most intriguing celestial bodies in our solar system.